What is Buddhism
Buddhism is one of the world’s major spiritual traditions. It began over 2,500 years ago in ancient India with a man named Siddhartha Gautama. He later became known as Shakyamuni Buddha. The word buddha means “the awakened one.”
Buddhism teaches us how to live with kindness, wisdom, and awareness. It helps people understand the nature of suffering, why it happens, and how we can overcome it to find inner peace.

Key concepts of Buddhism
The truth of suffering
The cause of suffering
The end of suffering
The path to end suffering

Who was Shakyumuni Buddha?
Shakyamuni Buddha was born a prince in what is now Nepal or northern India. Even though he had a comfortable life, he saw that people around him faced sickness, aging, and death. This led him to leave his palace in search of answers.
After many years of reflection and meditation, he gained insight into the nature of life and suffering. From then on, he spent the rest of his life sharing what he had learned, helping others find peace and purpose in their own lives.
What does a Buddha mean?
The word buddha in Sanskrit means “the awakened one.” It refers to someone who has fully awakened from spiritual ignorance and achieved complete freedom from suffering. A buddha sees reality with perfect clarity, understands the true nature of existence and has transcended the inner conflicts that cause suffering in life.
Buddhism teaches that this potential exists in everyone, and through practices, we can gradually discover and activate it.
How Did Buddhism Spread
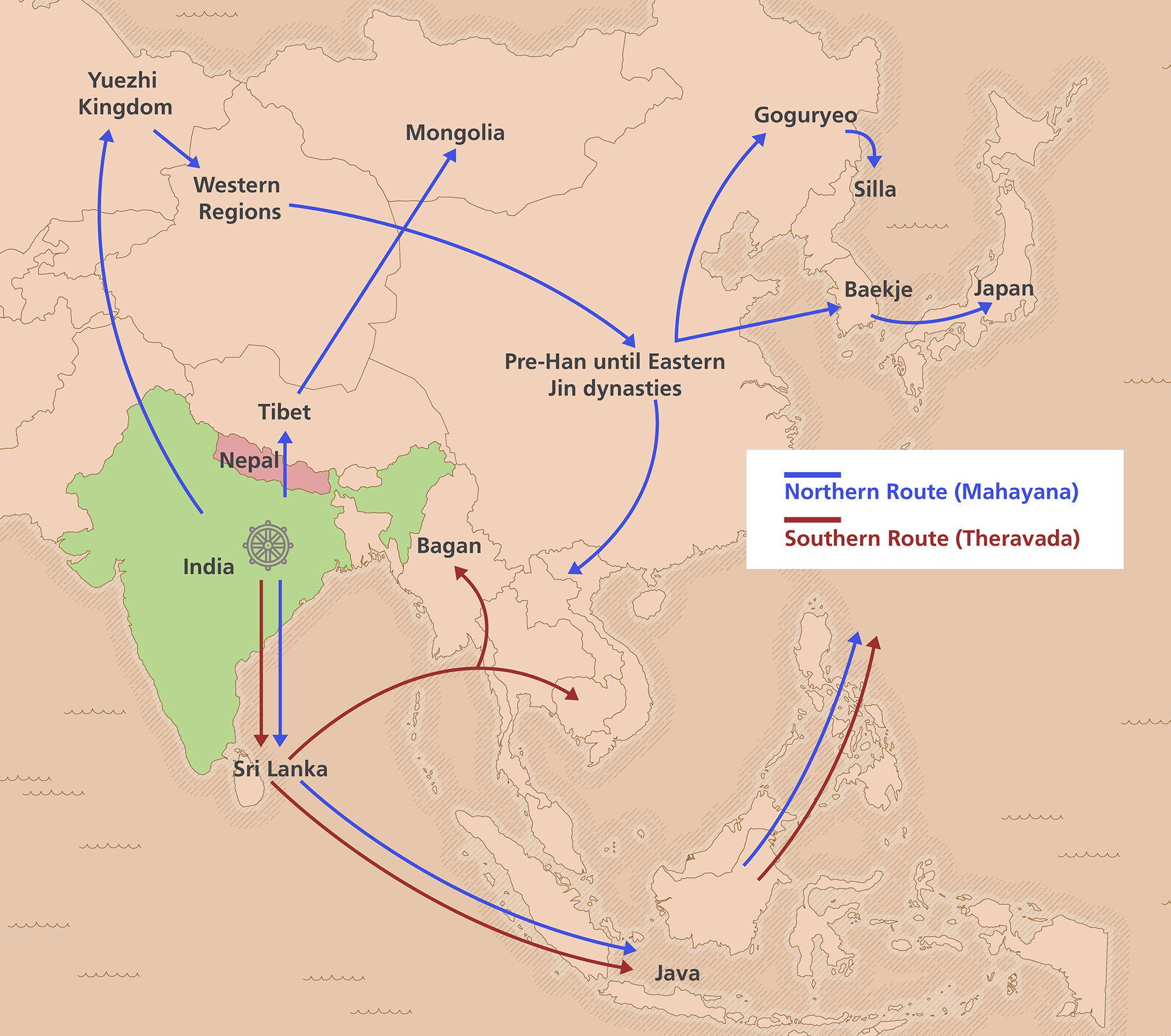
After the Buddha’s passing, his teachings were shared by his disciples and gradually spread across Asia through two main routes—a southern route and a northern route.
The Routes
The Southern Route brought Theravada Buddhism from India to Sri Lanka, and then to Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, and parts of Southeast Asia, including the Malay Peninsula.
The Northern Route spread Mahayana Buddhism through Nepal and Tibet, into Central Asia, and later into China, Korea, and Japan.
As Buddhism travelled through different cultures, it took on new forms while keeping its core values.
Schools of Buddhism
There are 3 main schools of Buddhism
Theravada
Mahayana
Esoteric
(also known as Esoteric Buddhism)
Esoteric Buddhism is a system of teachings, rituals, mantras and meditation techniques put together over a period of time. This tradition emphasises that everyone already has the potential for enlightenment inside them—this is called buddha nature. It is our true self, the part of us that naturally wants to escape suffering and live with love, joy, and wisdom. Buddha nature is the inner goodness that all living beings have, even if they don’t realize it yet.

What are the sacred texts?
Shakyamuni Buddha gave his disciples his final teaching in the form of the Mahaparinirvana Sutra, meaning “The Sutra of Great, Final Nirvana.” Both a Mahayana and Theravada version of this sutra exist, but they are quite different in their content. The Mahayana version of the sutra emphasizes using every opportunity to practice, and states that both lay and monastic followers can attain the awakening of buddhahood in this lifetime. Inspired by the inclusive aspect of this sutra, Shinjo Ito, the founder of Shinnyo-en, chose the Mahaparinirvana Sutra as the core text for the tradition.